(本文最初发布在掘金 https://juejin.cn/post/7242312269887914041)
学习 Linux 内核的第一步就是下载 Linux 内核代码, 然后进行编译与运行.
下载内核源代码
内核源码除了 Linus 的官方 https://github.com/torvalds/linux git, 还有各家发布版的 Linux 内核. 最好去发布版的内核去下载, 这样编译过程中不容易出错.
我的 Linux 机器是 Ubuntu 22.04 TLS, 所以根据官方文档: https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Kernel/SourceCode, 可以 clone git 下载:
$ git clone --depth 1 -b master git://git.launchpad.net/~ubuntu-kernel/ubuntu/+source/linux/+git/jammy
这里为了减少下载文件的数量和大小, 选择只下载最新的代码, 只选择了master分支. 下载到 jammy 文件夹.
编译配置
编译之前先要安装编译内核需要的各种安装包:
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt upgrade -y
$ sudo apt install git fakeroot build-essential ncurses-dev xz-utils libssl-dev bc flex bison libelf-dev -y
配置并编译
$ cd jammy
# 此时并没有 .config 文件, 执行下面的命令会让你选择配置, 然后保存.
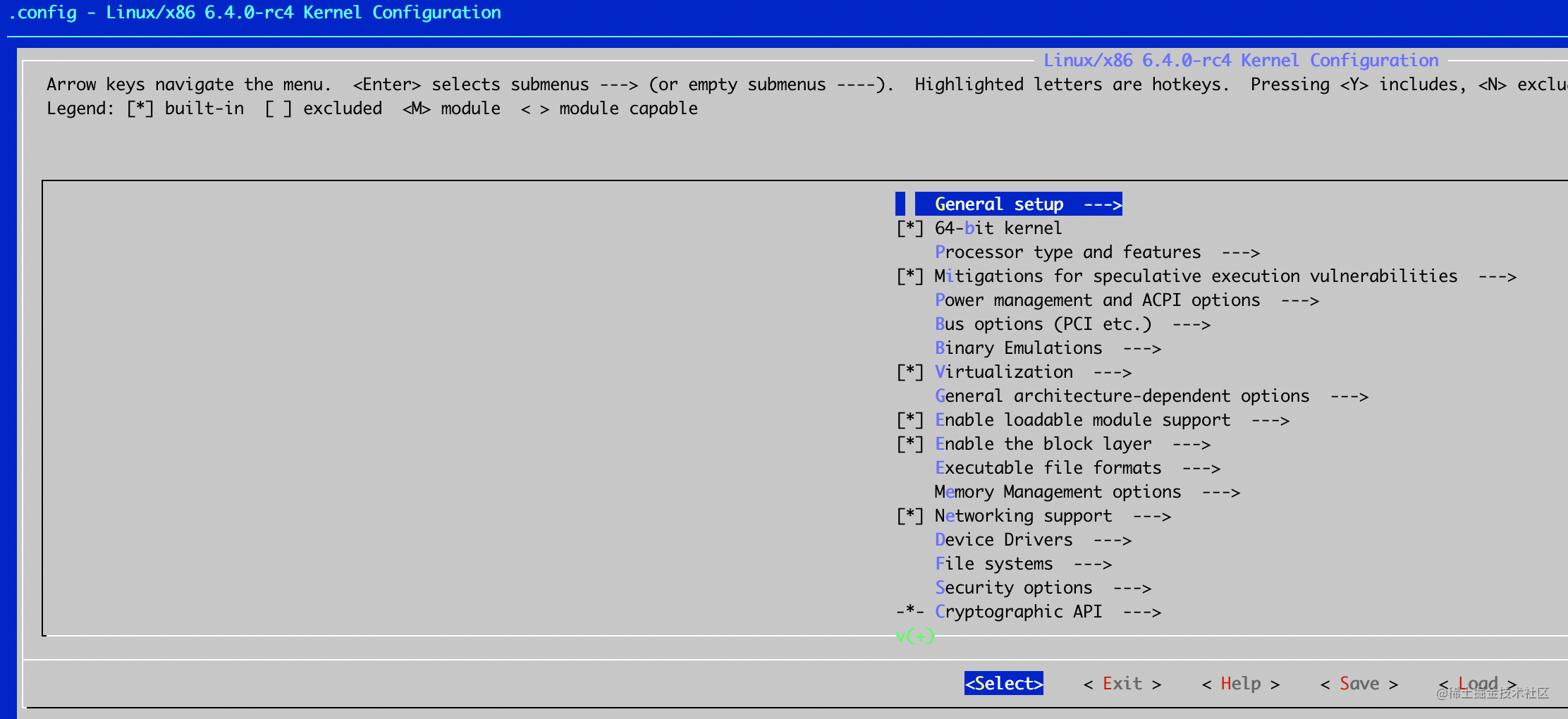
$ make menuconfig
# 生成 .config 文件
$ ls -lah .config
-rw-rw-r-- 1 sre sre 256K Jun 2 20:58 .config
我们可以看到 .config 文件里面的各种配置项目, 比如:
CONFIG_VERSION_SIGNATURE="Ubuntu 5.15.0-72.79-generic 5.15.98"
CONFIG_HAVE_KERNEL_GZIP=y
CONFIG_TSL2583=m
有些配置项表示一个纯文本的配置, 比如上面的版本号. 另外一些后面是 =y, =m 或者=n.
=y:当选项被设置为=y时,表示该选项将作为内核的一部分编译进内核映像(静态编译)。这意味着相关的功能将始终可用,并包含在生成的内核映像中。当系统启动时,这些功能将立即可用,无需加载额外的模块。选择=y是在构建内核时将特定功能编译到内核中的一种方式。=m:当选项被设置为=m时,表示该选项将作为可加载模块编译(动态编译)。这意味着相关的功能将编译为独立的模块文件(通常是以.ko为扩展名),并在需要时由内核加载。使用=m选项可以将特定功能作为模块构建,以便在运行时根据需要加载和卸载。
选择=y或=m取决于您对系统需求的权衡。如果您确定某个功能始终需要在内核运行时可用,并且不希望依赖额外的模块加载过程,则选择=y。如果您希望能够根据需要加载和卸载某个功能,并且不会一直使用该功能,则选择=m。
请注意,对于某些选项,可能还有其他设置,例如=n,表示将完全排除该功能的编译。这意味着相关的功能将在内核映像和模块中都不可用。选择特定的设置取决于您的需求和系统配置。
文字界面配置如下, 最后选择 Save 到 .config 文件.
编译:
$ make all -j 4 # 使用 4个线程编译, 可能要等很久, 最后生成内核文件 arch/x86/boot/bzImage
...
$ ls -lah arch/x86/boot/bzImage
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11M Jun 5 08:59 arch/x86/boot/bzImage
Kernel: arch/x86/boot/bzImage is ready (#1)
$ make help # 查看更多命令
如果遇到下面的出错:
sre@sre:~/work/exp/jammy$ make all -j 8
...
make[1]: *** No rule to make target 'debian/canonical-certs.pem', needed by 'certs/x509_certificate_list'. Stop.
make[1]: *** Waiting for unfinished jobs....
make: *** [Makefile:1900: certs] Error 2
可以参看 https://askubuntu.com/questions/1329538/compiling-the-kernel-5-11-11 去掉里面证书的部分:
# 可以看到当前的配置, 改成=“”
sre@sre:~/work/exp/jammy$ cat .config | grep CONFIG_SYSTEM_TRUSTED_KEYS
CONFIG_SYSTEM_TRUSTED_KEYS="debian/canonical-certs.pem"
测试启动内核
首先安装 qemu, 然后启动内核:
$ sudo apt install qemu-system-x86 -y
$ qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel bzImage -append "console=tty0 console=ttyS0" -nographic
SeaBIOS (version 1.15.0-1)
iPXE (https://ipxe.org) 00:03.0 CA00 PCI2.10 PnP PMM+07F8B340+07ECB340 CA00
Booting from ROM...
Kernel Offset: disabled
---[ end Kernel panic - not syncing: No working init found. Try passing init= option to kernel.
可以看到最后内核 panic, 因为没有任何 root 文件系统, 也没有 init 代码. 这时候, 我们可以通过 -initrd 来启动, 里面可以包含一个 busybox.
如何制作一个 initrd
使用 https://github.com/aweeraman/kernel-utils 提供的工具, 按照说明文档, 执行第一步 ./mk-initrd 就能生成 initramfs.cpio.gz, 里面包含了 initrc 和 busybox.
再次测试启动:
$ qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel bzImage -initrd initramfs.cpio.gz -append "console=tty0 console=ttyS0" -nographic
#这次成功启动
如何做一个最小的内核并启动进入命令行
制作最小内核
在 Linux 内核源代码根目录执行 make help, 你能看到各种有关配置的子命令, 比如:
defconfig: New config with default from ARCH supplied defconfig.allnoconfig: New config where all options are answered with no.allyesconfig: New config where all options are accepted with yes.tinyconfig: Configure the tiniest possible kernel.
这里我们关注的是 tinyconfig, 于是我们先清理一下, 然后使用 tinyconfig 生成 .config 文件, 然后制作 image, 最后使用 qemu 去执行:
$ make mrproper
$ make tinyconfig
$ make all -j 8
Kernel: arch/x86/boot/bzImage is ready
$ qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel bzImage -append "console=tty0 console=ttyS0 init=/bin/sh" -nographic
SeaBIOS (version 1.15.0-1)
iPXE (https://ipxe.org) 00:03.0 CA00 PCI2.10 PnP PMM+07F8B340+07ECB340 CA00
Booting from ROM..
最后发现日志停在 Booting from ROM.. 就没有任何消息了.
这是因为 tinyconfig 包含的驱动或者配置太少, 导致没有后续输出, 我们需要在 tinyconfig 的基础上添加一些配置.
添加配置
添加配置使用 make menuconfig 来修改, 最后保存就好.
- 64-bit kernel
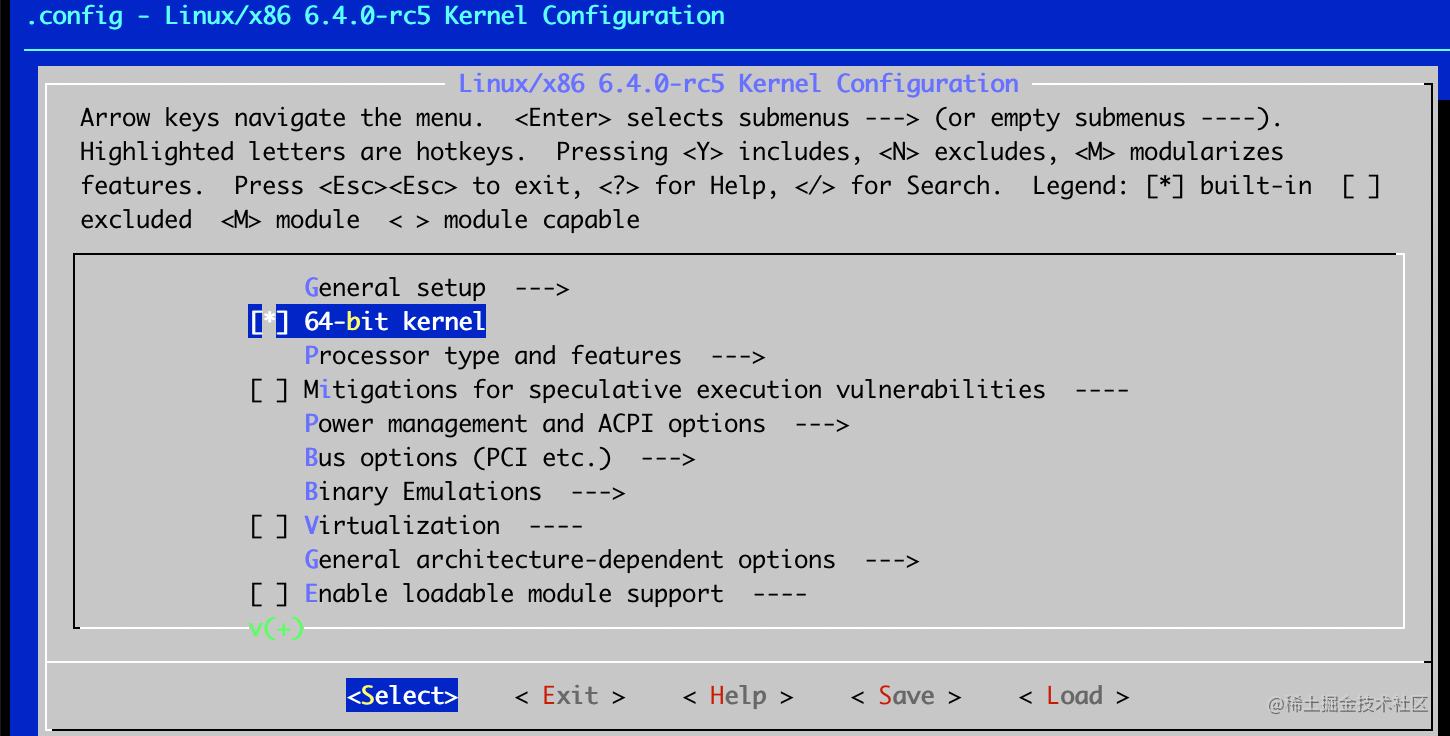
- Device Drivers -> Character devices -> Enable TTY
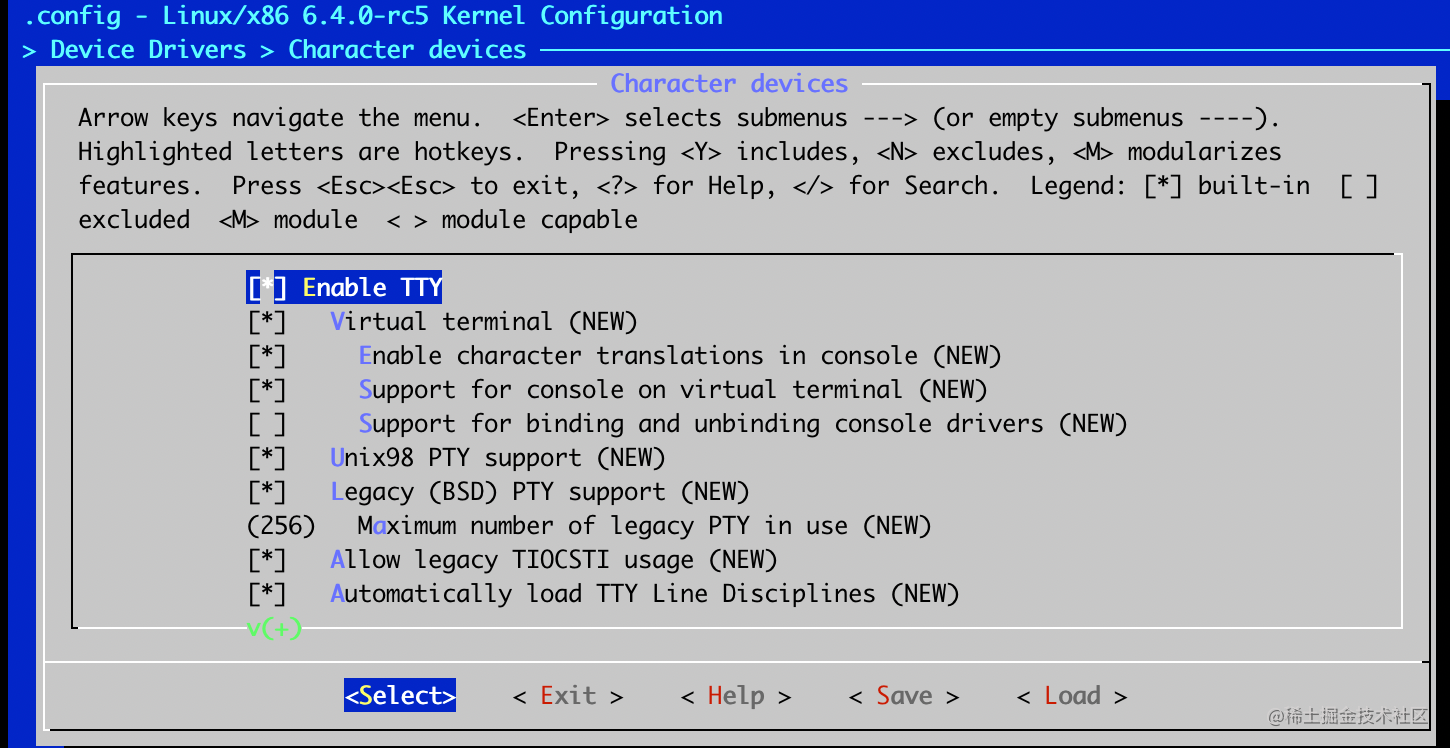
- Device Drivers -> Character devices -> Serial drivers -> 8250/16550 and compatible serial support -> Console on 8250/16550 and compatible serial port
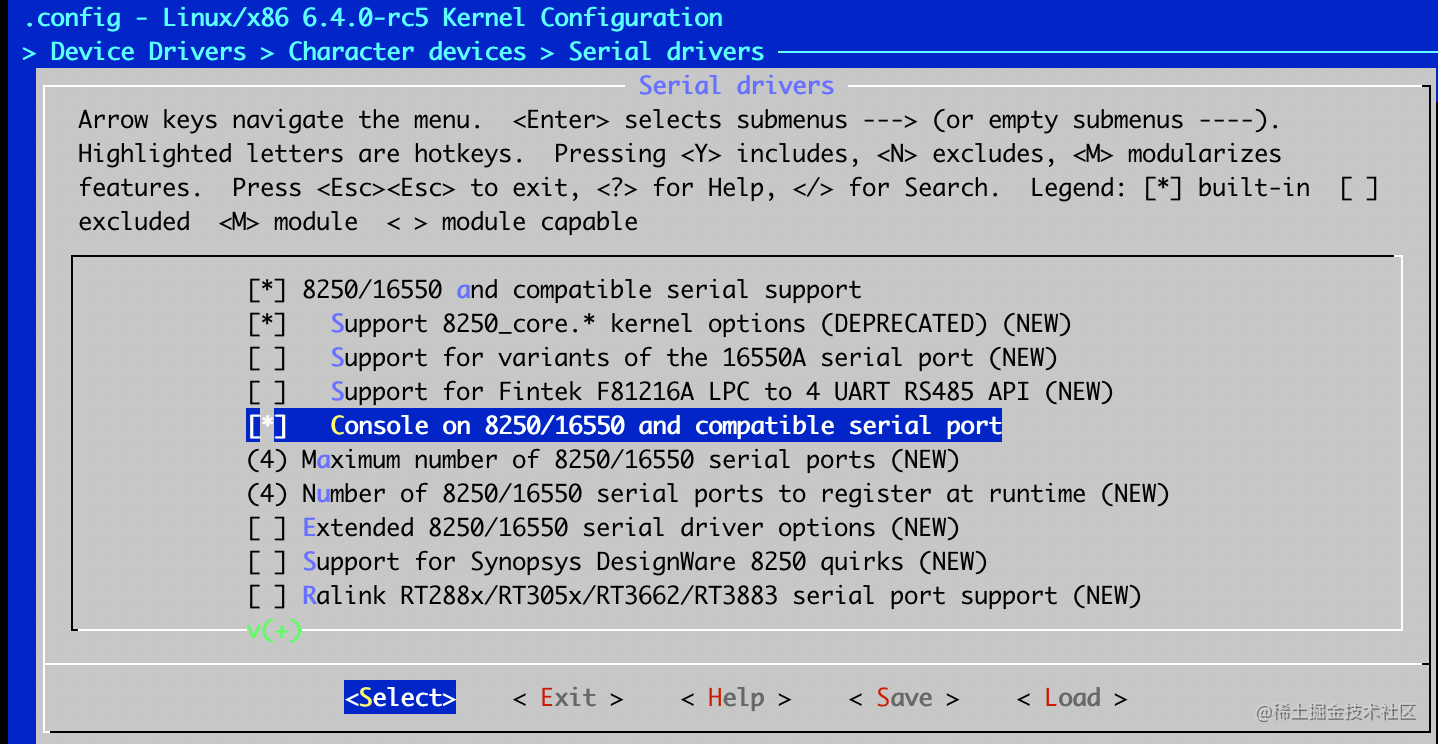
- General setup > Configure standard kernel features (expert users) -> Enable support for printk
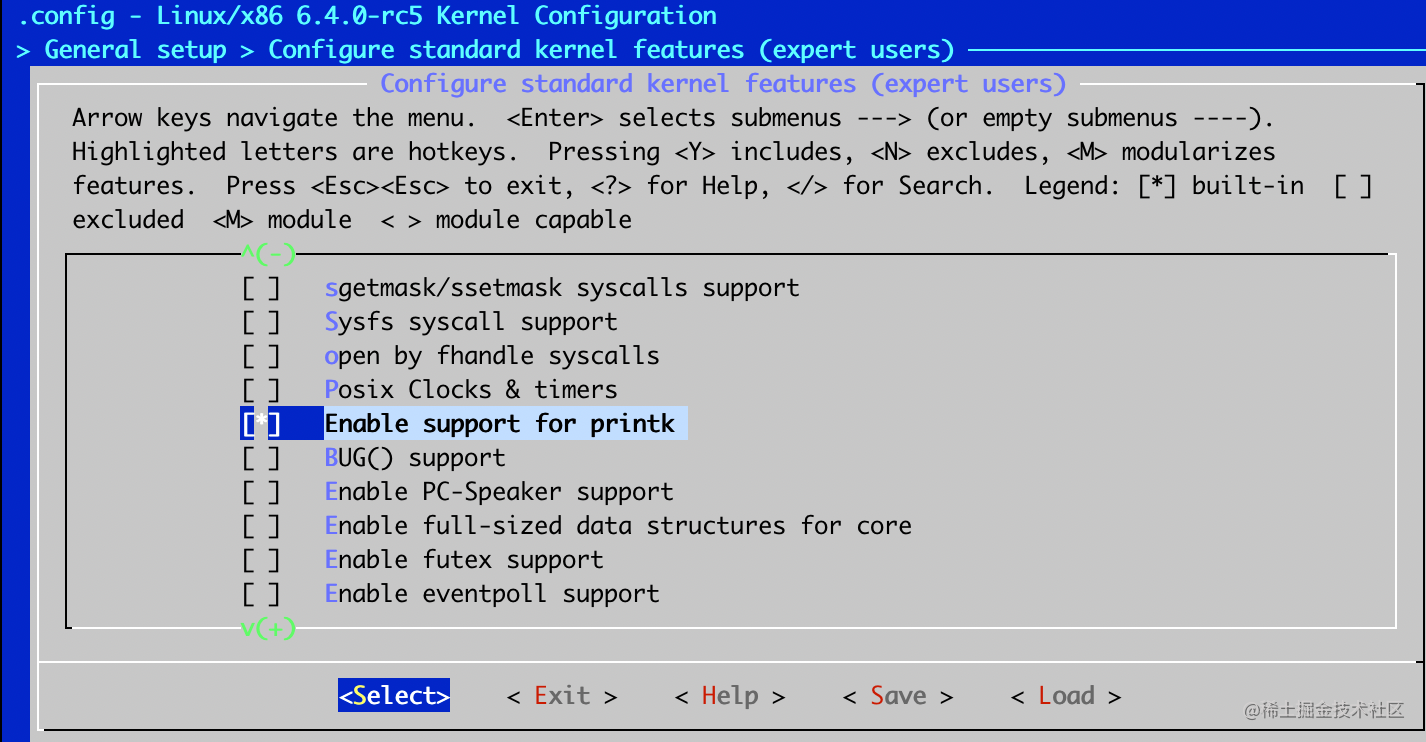
保存上面配置, 并且做一个新的image:
$ make all -j 8
$ qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel bzImage -append "console=tty0 console=ttyS0 init=/bin/sh" -nographic
SeaBIOS (version 1.15.0-1)
iPXE (https://ipxe.org) 00:03.0 CA00 PCI2.10 PnP PMM+07F8B340+07ECB340 CA00
Booting from ROM..
Run /bin/sh as init process
Kernel panic - not syncing: Requested init /bin/sh failed (error -2).
Kernel Offset: disabled
---[ end Kernel panic - not syncing: Requested init /bin/sh failed (error -2). ]---
可以看到 Kernel panic, 因为我们只是启动 kernel, 没有root 文件系统, 也没有使用 initrd 的ramdisk.
修改config 支持 initrd
使用 make menuconfig 继续修改
- General setup -> Initial RAM filesystem and RAM disk (initramfs/initrd) support
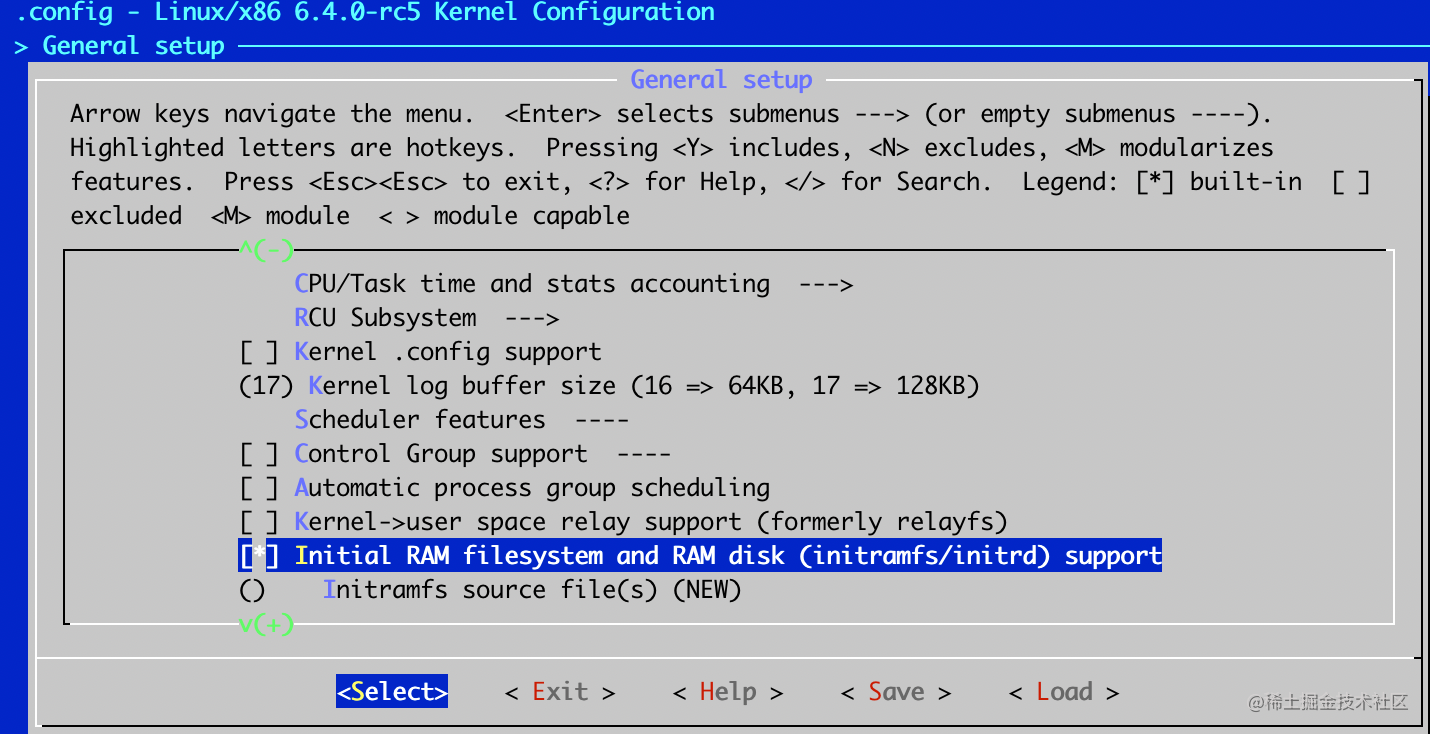
- Executable file formats -> Kernel support for ELF binaries
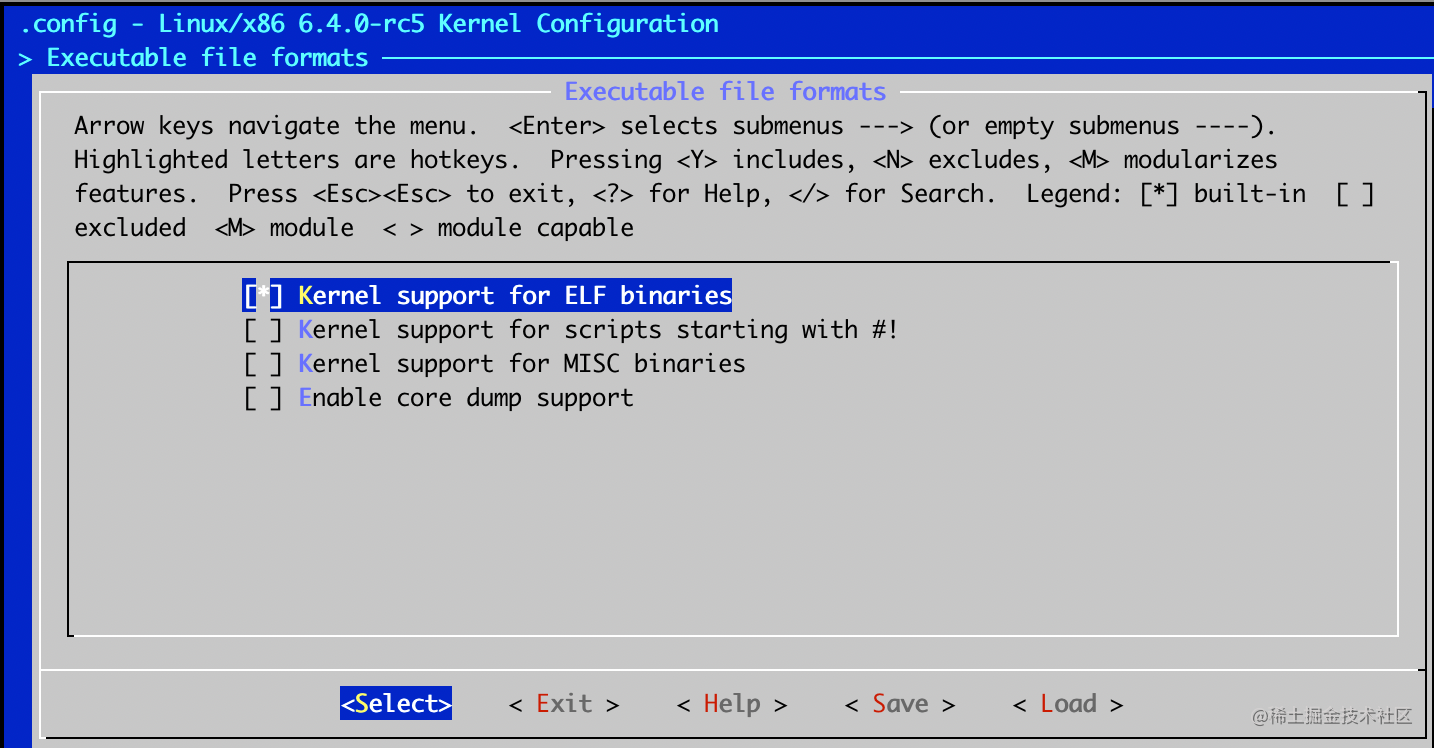
保存, 然后 make all -j 8 再次制作image, 然后运行:
$ qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel bzImage -initrd initramfs.cpio.gz -append "console=tty0 console=ttyS0 init=/bin/sh" -nographic
Run /init as init process
Failed to execute /init (error -8)
Run /bin/sh as init process
/bin/sh: can't access tty; job control turned off
/ # input: ImExPS/2 Generic Explorer Mouse as /devices/platform/i8042/serio1/input/input2
clocksource: tsc: mask: 0xffffffffffffffff max_cycles: 0x311fac54234, max_idle_ns: 440795352581 ns
clocksource: Switched to clocksource tsc
uname -a
Linux (none) 6.4.0-rc5+ #3 Wed Jun 7 08:19:32 PDT 2023 x86_64 GNU/Linux
/ # ls /bin/
...
/ # ps aux
PID USER TIME COMMAND
可以看到 kernel 启动后执行了 /bin/sh, 我们使用 uname能看到 kernel 的版本号, 但是ps 没有任何输出. 那是因为我们没有挂载 proc 文件系统. 同时执行挂载 proc 文件系统的脚本在 initramfs.cpio.gz 内部的 init 文件里, 它是一个 shell, 所以要使 kernel 支持 shell 的 #!.
再次通过 make menuconfig 修改配置:
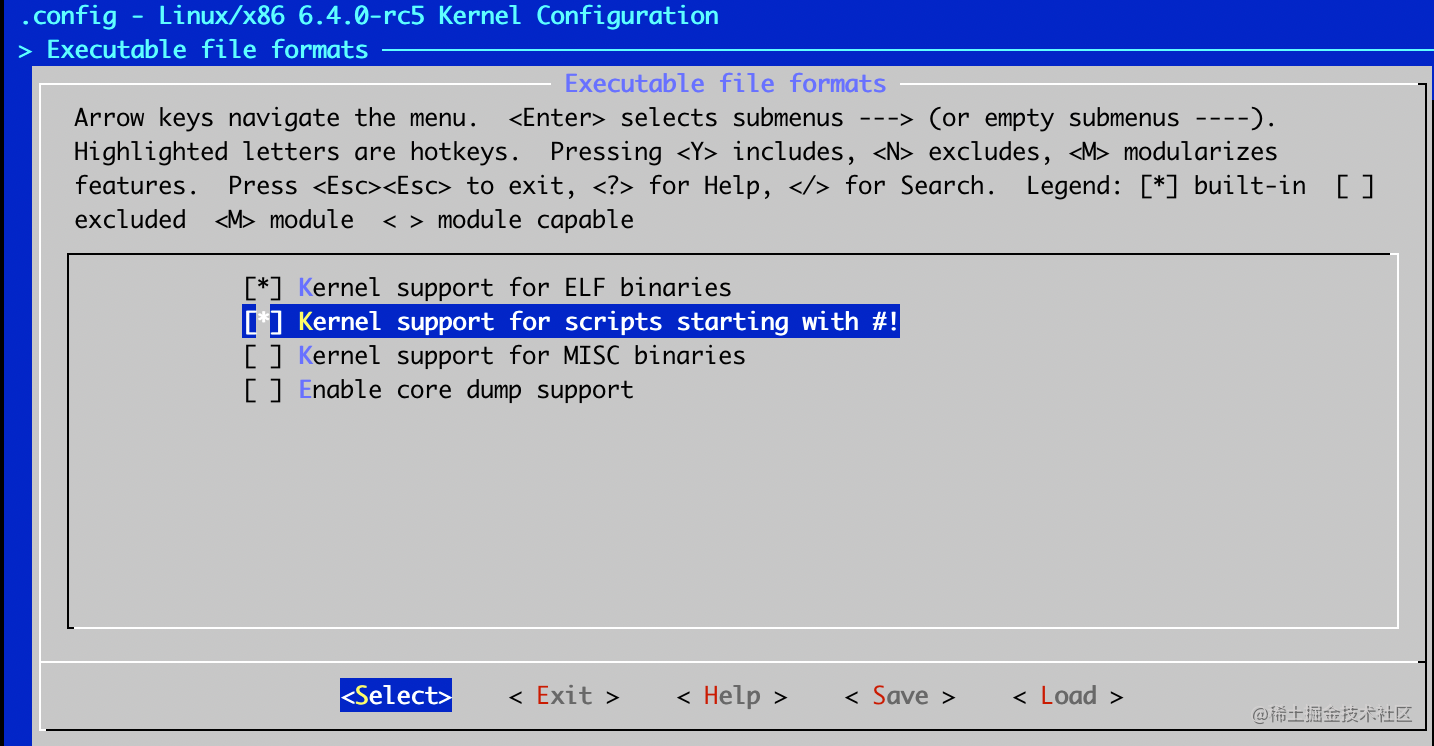
- Executable file formats -> Kernel support for scripts starting with #!
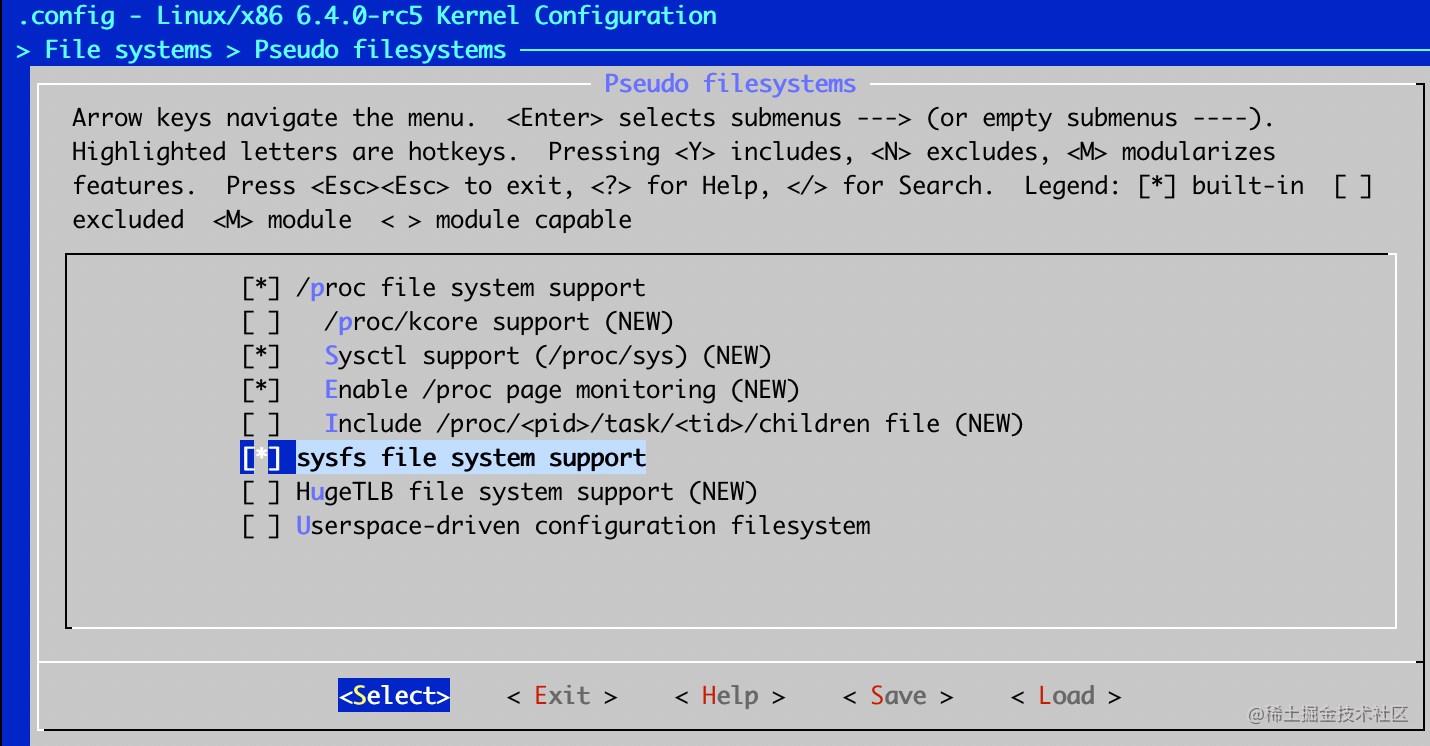
2. File systems > Pseudo filesystems -> (/proc file system support & sysfs file system support)
修改完保存, 然后重新制作 image, 并且运行:
$ qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel bzImage -initrd initramfs.cpio.gz -append "console=tty0 console=ttyS0 init=/bin/sh" -nographic
ps
PID USER TIME COMMAND
1 0 0:00 {init} /bin/sh /init
2 0 0:00 [kthreadd]
3 0 0:00 [kworker/0:0-eve]
4 0 0:00 [kworker/0:0H]
5 0 0:00 [kworker/u2:0-ev]
6 0 0:00 [mm_percpu_wq]
7 0 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0]
8 0 0:00 [oom_reaper]
9 0 0:00 [writeback]
10 0 0:00 [kswapd0]
11 0 0:00 [kworker/u2:1-ev]
12 0 0:00 [kworker/0:1-eve]
13 0 0:00 [kworker/u2:2-ev]
14 0 0:00 [kworker/0:2]
19 0 0:00 sh
20 0 0:00 ps
如何制作一个可运行的 ISO 文件
创建文件结构并且复制数据
$ mkdir -p iso/boot/grub
$ cp bzImage iso/boot/
$ cp initramfs.cpio.gz iso/boot/
创建 grub.cfg 文件
$ vim iso/boot/grub/grub.cfg
set default=0
set timeout=10# Load EFI video drivers. This device is EFI so keep the
# video mode while booting the linux kernel.
insmod efi_gop
insmod font
if loadfont /boot/grub/fonts/unicode.pf2
then
insmod gfxterm
set gfxmode=auto
set gfxpayload=keep
terminal_output gfxterm
fimenuentry 'myos' --class os {
insmod gzio
insmod part_msdos
linux /boot/bzImage init=/bin/sh console=ttyS0 console=tty0
initrd /boot/initramfs.cpio.gz
}
安装 xorriso, mtools 并且制作 ISO image:
$ sudo apt install xorriso mtools -y
$ grub-mkrescue -o myos.iso iso/
$ ls -lah myos.iso
使用 Qemu 测试新的 ISO image
$ qemu-system-x86_64 -boot d -cdrom myos.iso -nographic